
eGRID
迅速な設置。
柔軟性。
従来のカーボン ファイバー グリッドでは、カーボン ファイバーの表面は多かれ少なかれ含浸剤で覆われているため、電気的に簡単に接続できません。弊社の solidian FLEX GRID をベースに、導電性が重要な特殊な用途向けに導電性表面処理を施したカーボン グリッド solidian eGRID を開発しました。この新しい機能は、陰極腐食防止 (CCP) システム、監視、壁および床暖房システムで特に役立ちます。
Product Features
solidian eGRID は、低接触抵抗で直接電気接続し、グリッド構造内で電流を均等に分散します。グリッドの従来のポリマー含浸は絶縁層のように機能しますが、solidian eGRID の新しい導電性表面処理により、カソード保護システムや監視の目的で必要な横方向に電流を逃がすことができます。これらの新しい特性にもかかわらず、優れた機械的特性と柔軟性は通常どおり維持されています。
スケッチ画像は、平面と横方向に流れる電流を示しています。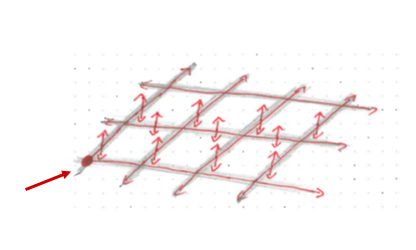
solidian eGRID は巻き上げることができ、当社の新しい solidian CARGO システムで建設現場に簡単に輸送できます。
幅 2.50 m で最大 300 m の長さを巻き取りリールに保管し、簡単に巻き戻すことができます。さらに、solidian CARGO システムには切断ナイフとメーターカウンターも設置されており、正確で迅速な切断が可能です。ロール状の solidian eGRID を使用すると、長さ方向の補強材の重なりを最小限に抑えるか、完全に回避できます。
reinforcements for the future generations
Reference project
Product Applications
陰極腐食保護 (CCP)
従来の陰極腐食保護システムでは、コンクリート構造物に保護電流が誘導されます。その結果、腐食を引き起こす塩化物イオンが補強材から陽極に移動します。これにより、塩化物イオンと鋼鉄表面が分離され、さらなる腐食のリスクが大幅に軽減されます。標準的な用途では、非常にコストのかかる不活性チタン陽極が使用されます。
solidian eGRID は、これらのチタン陽極を完全に置き換えることができます。
柔軟性と導電性を備えた炭素繊維グリッドは、高密度のネットワークを形成し、比表面積が大きいため、コンクリートに電流を均等に分散できます。
チタンベースのソリューションとは異なり、solidian eGRID は二次補強材としても機能し、コンクリートの亀裂の進行を制御するのに役立ちます。説明した用途は、長年にわたって試行され、テストされてきました。
水分の監視
導電性炭素繊維補強材は、道路橋の表面保護システムの損傷領域を早期に検出するなど、リアルタイムの水分監視システムを設置するためにも使用できます。
校正曲線は、2 つの炭素層間の電気抵抗を測定することでモルタルの水分含有量を決定するために使用されます。抵抗の低下は防水材の漏れを示します。抵抗が低いということは、モルタルの水分飽和度が高いことを意味します。
このアイデアは、「SMART-DECK」研究プロジェクトの一環として初めてテストされ、予防的な陰極腐食保護システムと組み合わせられました。これは漏れのある領域でのみ作動しました。「SMART-DECK」の詳細については、こちらをご覧ください。
コンクリート表面の加熱
導電性二次補強材は、さまざまな用途で興味深いものになる可能性があります。たとえば、導電性炭素補強材を使用してコンクリート表面を加熱できます。これは、滑走路、積込ランプ、または傾斜のあるアクセス領域の除氷に興味深いものです。
同じことが、壁の加熱を可能にする Solidian eGRID 層を備えた炭素強化石膏にも当てはまります。このタイプの表面加熱により、特に快適な室内環境が確保され、熱損失が減少します。
当社は、特に電気設備の運用を目的とした、加熱コンクリート表面の分野でパートナーを探しています。ご興味がございましたら、ぜひご連絡ください。
- Performance Enhancement
- Handling and Logistics
- Compliance and Compatibility
- Application and Installation
- Durability and Resistance
- Sustainability and Environmental Impact
- Is solidian GRID suitable for replacing corroded steel reinforcement?
- How does solidian GRID contribute to system durability when used with mortars?
- Can solidian GRID conform to curved surfaces during installation?
- How does the weight of solidian GRID affect transportation and installation?
- Is there an Environmental Product Declaration available for solidian GRID and solidian REBAR?
- Has solidian GRID received official building approvals?
- With which types of binders is solidian GRID compatible?
- Is solidian GRID approved for use in standard concrete applications?
- What is the minimum thickness required for concrete layers using solidian GRID?
- Can solidian GRID be used to reinforce existing concrete structures?
- What is the expected lifespan of solidian GRID in wastewater applications?
- How does solidian GRID perform in acidic environments?
- How does solidian GRID contribute to sustainable construction?
- Resource efficiency: By minimizing the need for extra concrete cover, solidian GRID conserves materials such as cement and aggregates, contributing to resource efficiency.
- Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs): solidian provides transparent data on the environmental impact of their products through EPDs, facilitating informed decision-making for sustainable building projects.
Solidian Kelteks - Reduced CO₂ emissions: The use of solidian GRID in construction can lead to significant reductions in CO₂ emissions due to decreased material usage and enhanced durability, which extends the lifespan of structures and reduces the need for repairs.
frequently asked questions
Yes, in cases where steel reinforcement has corroded, solidian GRID can serve as a substitute for structural reinforcement. The existing corroded steel can remain in place and be covered with a new layer of carbon-reinforced mortar, restoring structural integrity.
When combined with high-quality mortars, solidian GRID significantly enhances the overall durability of the system, providing a robust solution for demanding environments.
Yes, solidian GRID strikes a balance between stiffness and flexibility, allowing it to be applied to curved surfaces with diameters greater than 800mm.
The lightweight nature of solidian GRID facilitates easy transportation, even through sewage tunnels, and simplifies the installation process, reducing labor and equipment requirements.
Yes, a certified Environmental Product Declaration (EPD) is available for both solidian GRID and solidian REBAR. The EPD provides transparent and verified information about the environmental impact of these products throughout their life cycle, supporting sustainability assessments in construction projects.
Yes, solidian GRID has obtained the General Building Approval (abZ) from the German Institute for Building Technology (DIBt). This approval authorizes its use as carbon reinforcement grids in construction, ensuring compliance with national building standards.
solidian GRID is versatile and works with a range of binders, including Portland Cement, Calcium Aluminate Cements, and Geopolymer Cements.
solidian GRID holds German Approval as reinforcement for EN 206 concretes, supporting its compatibility with various mortar systems, including those adhering to DIN 19573.
Concrete layers reinforced with solidian GRID can be as thin as 20mm, as no additional concrete cover is needed to protect the reinforcement from corrosion.
Yes, solidian GRID can be applied as an additional layer over existing steel-reinforced concrete. When combined with solidian ANTICRACK, it offers enhanced crack-limiting properties, providing extra protection to the underlying steel reinforcement.
Classified under XWW4, solidian GRID ensures long-term performance for over 50 years, making it a durable choice for long-term infrastructure projects.
solidian GRID is fully resistant to severe acidic conditions, including environments with pH levels as low as 0. It has successfully passed tests in accordance with DIN 19573 standards for pH 0 and pH 1.
solidian GRID enables the design of thinner concrete layers (greater than 20mm) without requiring additional concrete cover for reinforcement protection. This reduction in material usage leads to lower resource consumption and a diminished environmental footprint, supporting more sustainable construction practices.
Additional information:




