To stop climate change and to protect our planet, we all must change our behaviour
The construction sector is responsible for a significant proportion of global CO2 emissions and is often regarded as one of the biggest emitters. This is due to various factors such as energy consumption during the construction process, the production of building materials and the energy consumed during the construction. However, there are increased efforts to reduce the carbon footprint of the construction sector. Sustainable construction involves the use of more environmentally friendly building materials, energy-efficient technologies and the integration of renewable energy in buildings.
Carbon concrete is one of these sustainable building materials

Why?
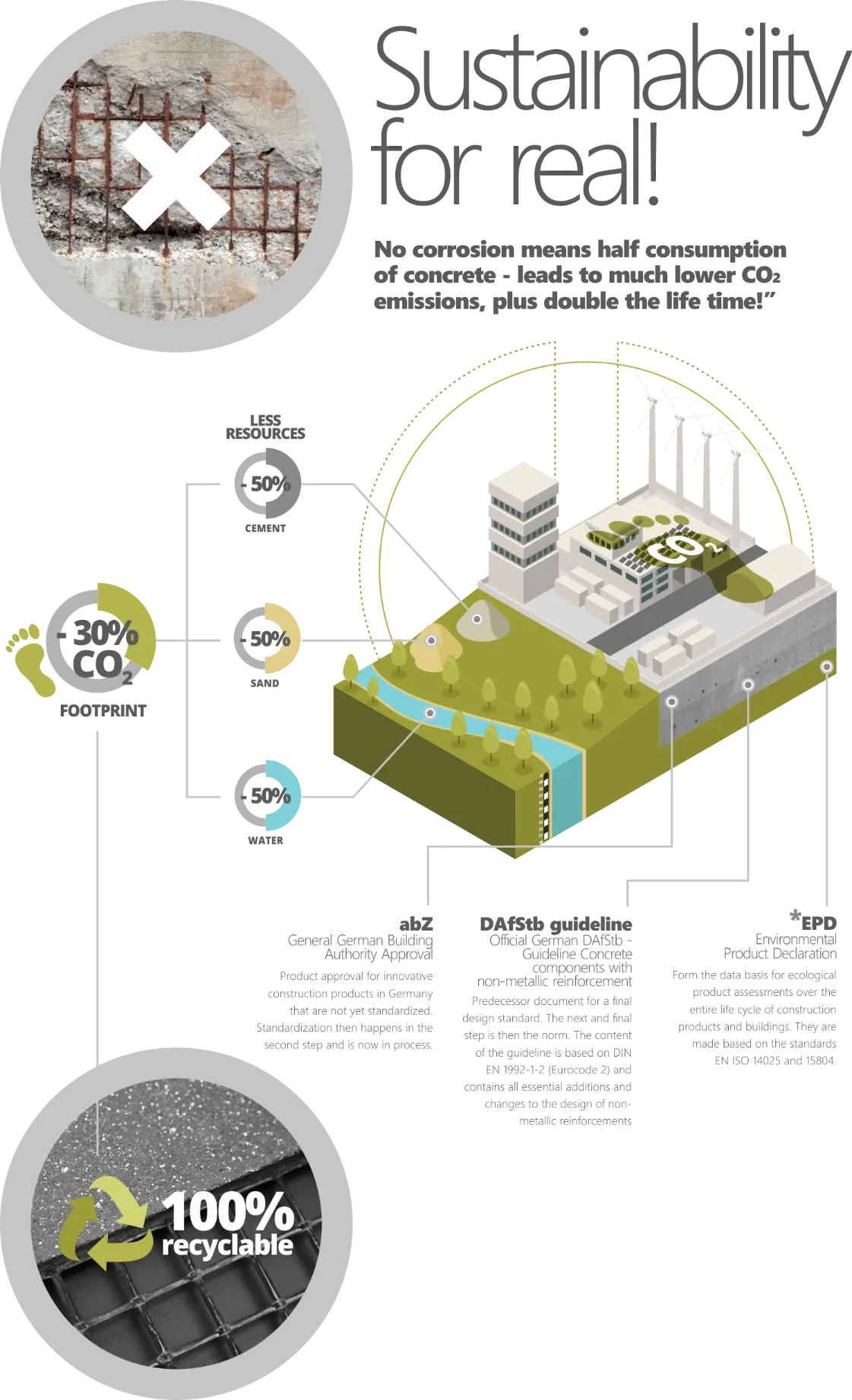
Corrosion-free reinforcement
= less concrete cover required
= less material & resources required
= less CO2 emissions
Info about Cement
The production of building materials such as cement and steel often requires energy-intensive processes. Cement is produced by heating a mixture of limestone, clay and other materials at very high temperatures (approx. 1450°C) in a rotary kiln. This process is known as cement clinker production and is extremely energy-intensive. It produces significant CO2 emissions, mainly due to the burning of fuels to heat the raw material and the chemical reactions that occur during cement clinker production. It is estimated that the cement sector is responsible for around 7-8% of global CO2 emissions worldwide.
When building with carbon concrete, we can be much more economical with cement as a resource, because basically less concrete is needed for construction because the reinforcement does not corrode. Therefore, unlike with steel reinforcement, no thick concrete cover is required for protection.
The ecological footprint of our products is presented transparently
- The word'd first EPD for a carbon reinforcement mesh
- The EPD serves as a data basis for evaluations of components and buildings as well as sustainability certification systems for buildings
- Despite the high CO2 equivalents of the solidian GRID carbon reinforcement as such, massive reductions in CO2 equivalents can be achieved in the component (see life cycle assessment examples). This is achieved because not only the initial CO2 emissions, but the entire life cycle of the building is considered
>>> DOWNLOAD HERE
Green Building Broschure
- Everything about sustainable concrete construction summarized for you in our brochure!
>>> DOWNLOAD HERE








